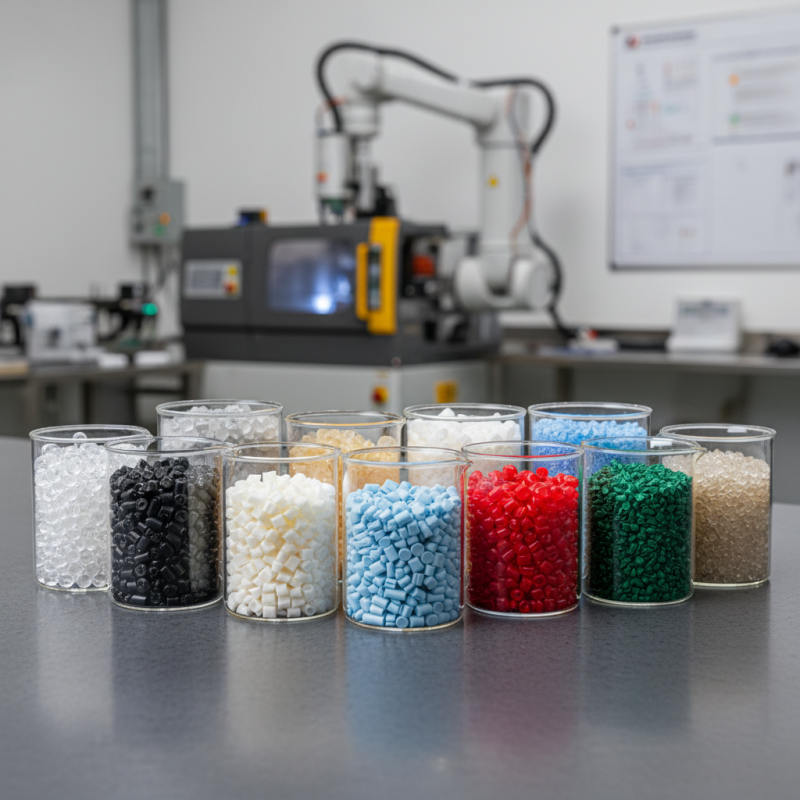
Injection molding is a vital process in manufacturing. It allows for the rapid production of complex parts in various industries. A crucial aspect of this process is the selection of appropriate injection molding materials. Different materials bring unique properties and benefits. Understanding these materials is essential for achieving the desired performance and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the right injection molding materials can be challenging. Each type has its advantages and limitations. For instance, some materials offer high strength, while others provide flexibility or resistance to chemicals. This diversity can both simplify and complicate decision-making. Designers and engineers must carefully weigh their choices based on the project's requirements.
Many factors influence material selection. Considerations include production volume, environmental conditions, and product lifespan. It’s not uncommon to see mistakes in material choice leading to costly reworks. Learning from these missteps can guide better decisions in the future. Knowing the top injection molding materials helps avoid pitfalls and enhance product quality.

Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process. It creates products by injecting molten material into a mold. This method is essential in various industries, from automotive to consumer goods. Understanding the injection molding process helps businesses optimize production efficiency. It also enhances product quality.
Tips: Always consider material selection carefully. The right material affects durability and cost.
Molds have an important role. A well-designed mold can significantly improve product outcomes. However, imperfections in the mold can lead to defects. It's vital to test and refine designs.
Tips: Regular maintenance of molds is crucial. Neglected molds can produce inconsistent results over time. A focus on precision can save time and resources down the line.
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Melting Temperature (°C) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | 0.93 - 0.97 | 20 - 30 | 120 - 180 | Packaging, containers |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 0.85 - 0.91 | 30 - 50 | 160 - 170 | Automotive parts, textiles |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 1.04 - 1.06 | 30 - 50 | 240 - 260 | Consumer goods, toys |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | 1.30 - 1.45 | 50 - 70 | 75 - 105 | Pipes, fittings, flooring |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 1.04 - 1.08 | 40 - 50 | 210 - 245 | Electronic housings, automotive |
| Nylon (PA) | 1.13 - 1.15 | 50 - 85 | 190 - 220 | Gears, bearings, textiles |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 1.20 - 1.22 | 60 - 70 | 230 - 270 | Transparent panels, automotive |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | 1.38 - 1.40 | 50 - 70 | 250 - 260 | Bottles, containers |
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | 0.85 - 1.20 | 15 - 30 | 200 - 220 | Seals, gaskets, soft touch parts |
| Polylactic Acid (PLA) | 1.23 - 1.25 | 50 - 70 | 160 - 180 | Biodegradable products, 3D printing |
Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process. It is widely used due to its efficiency and versatility. Some polymers stand out for their suitability in this process. Understanding these materials is crucial for any professional in the field.
Commonly used polymers include ABS, polyethylene, and polypropylene. ABS is known for its strength. It is resistant to impact, making it ideal for various applications. Polyethylene, on the other hand, is known for its flexibility. It is lightweight and often used in packaging. Polypropylene offers high chemical resistance and toughness. These properties make it a popular choice in automotive parts.
Tips: Always check the material specifications. Not all polymers are suitable for every project. Different applications may require specific characteristics. Test samples can help evaluate performance.
One must also consider environmental factors. Some materials may not perform well under certain temperatures or humidity levels. Reflecting on project needs can lead to better material choices. Remember, the right polymer can enhance product durability and cost-effectiveness.
When considering injection molding, choosing the right material is crucial. There are various options available, each with unique properties. For instance, ABS is popular for its balance between durability and cost. It is lightweight and can withstand impact, making it ideal for many applications. However, its susceptibility to UV light can be a drawback.
Polycarbonate is another notable material. It offers high transparency and excellent mechanical strength. This makes it suitable for parts that require visibility and toughness. Yet, polycarbonate may absorb moisture over time, which can affect its performance.
Then there is polypropylene, known for its flexibility and chemical resistance. It is often used in medical applications and packaging. However, its lower tensile strength can limit its use in heavy-duty components. These materials demonstrate that while there are great options, each has its vulnerabilities and considerations. Understanding these properties helps in making informed decisions for specific projects.
Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process. Choosing the right material can significantly impact production efficiency and product quality. Different materials offer unique properties, making them suitable for specific applications.
For instance, polypropylene is widely used in packaging. It is lightweight and resistant to moisture. This helps reduce shipping costs. In fact, studies show that nearly 20% of all injection-molded parts utilize polypropylene. Its flexibility also allows for complex designs, appealing to a broad range of industries. However, its lower strength may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Another material to consider is ABS. It is known for toughness and impact resistance. ABS is often used in consumer electronics. This material provides a smooth finish, essential for aesthetic products. Approximately 15% of injection-mold jobs involve ABS. However, ABS can be susceptible to environmental stress cracking, which must be considered in design phases. A balance between its benefits and limitations is necessary to avoid issues in end products.
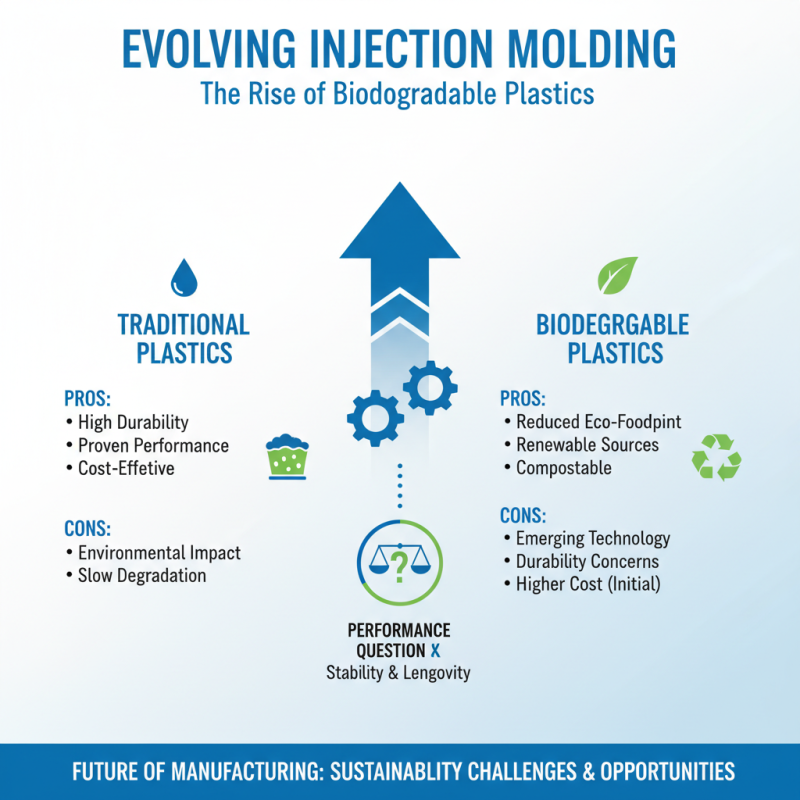
The world of injection molding is evolving. New materials are emerging, and each holds promise. Biodegradable plastics are gaining traction. They reduce environmental impact. Many manufacturers are exploring these options. However, their performance still raises questions. Stability and durability are often not at par with traditional materials.
Another trend is the use of composites. They combine strength and light weight. This can lead to innovative designs in various industries. However, the manufacturing process can be complex. Balancing cost and performance remains a challenge. Additionally, additive manufacturing is being integrated with injection molding. This could lead to more sophisticated applications and designs. Nevertheless, it requires a shift in traditional thinking.
Sustainability is not just a buzzword. It influences material selection significantly. Many factories are aiming to reduce waste. Yet, transitioning to new materials often involves experimentation and risks. The path forward must include collaboration and testing. Understanding how these materials behave in real-world conditions is essential. The future will likely see a blend of innovation and reflection on past practices.