Rotational molding, a versatile and innovative manufacturing process, has increasingly gained recognition for its ability to produce a wide array of hollow plastic products. This technique, which involves heating plastic in a mold while rotating it along two axes, allows for the creation of complex shapes with uniform wall thickness and excellent structural integrity. As industries continue to seek efficient and cost-effective methods for product development, mastering rotational molding has become essential for manufacturers aiming to remain competitive in the market.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various techniques and tips that can elevate your understanding and execution of rotational molding. From selecting the right materials to optimizing mold design and production processes, these insights will provide you with the knowledge necessary to harness the full potential of this technique. By implementing these best practices, you can enhance product quality, reduce waste, and streamline operations, ultimately leading to a successful rotational molding endeavor. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the field, this guide will serve as a valuable resource in your journey to mastering rotational molding.
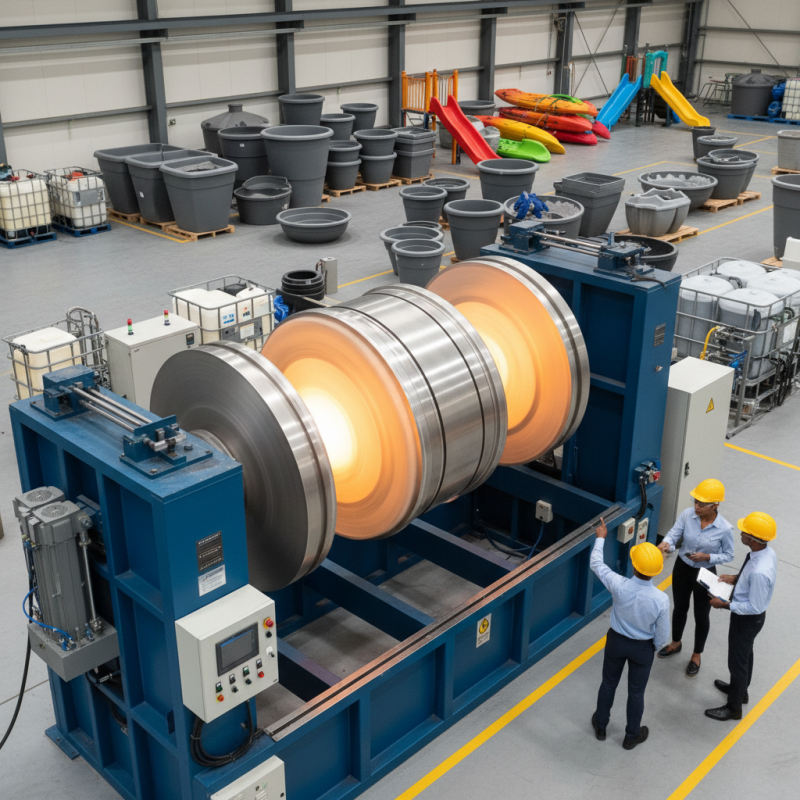

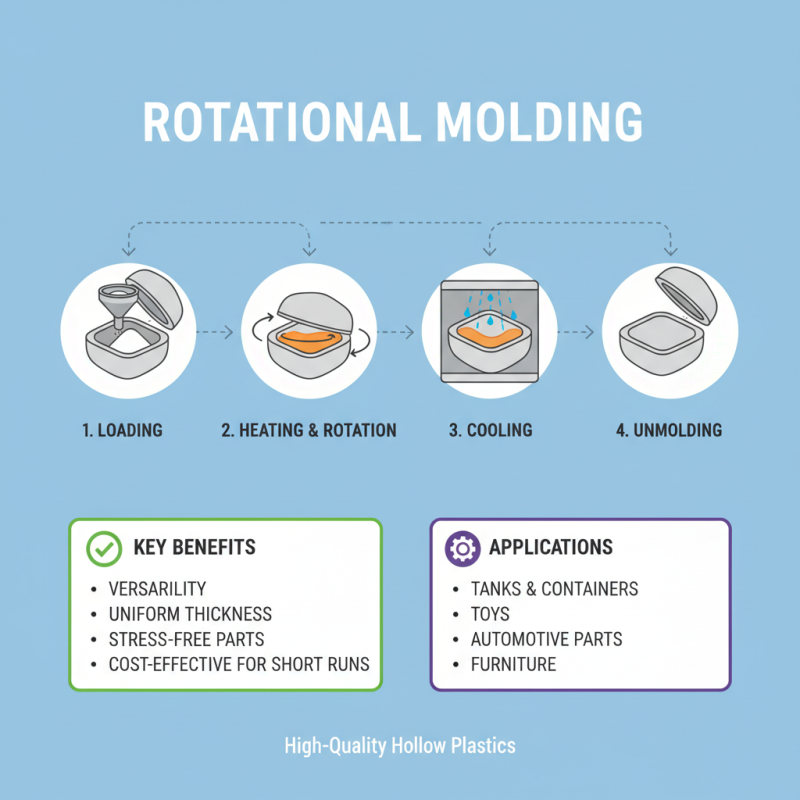
Rotational molding is a versatile manufacturing process that allows for the creation of hollow plastic parts through a unique heating and cooling technique. This method involves loading powdered plastic into a mold, which is then rotated along two axes as it is heated. The powder melts and coats the inner walls of the mold, forming a uniformly thick part once it cools. Understanding the fundamentals of this process can significantly enhance production efficiency and part quality, making it a popular choice across various industries.
One of the primary applications of rotational molding is in the production of large containers, tanks, and outdoor furniture. Its ability to create complex shapes without seams makes it ideal for products requiring durability and weather resistance. Additionally, the process can accommodate a wide range of materials, including polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC, offering flexibility tailored to specific requirements. By mastering the basics of rotational molding, manufacturers can leverage its strengths to innovate and improve their product offerings while maintaining cost-efficiency.
When mastering rotational molding, having the right equipment and materials is crucial for achieving optimal results. The essential machinery includes a rotational molding machine, which typically consists of two main components: a heating oven and a cooling chamber. The oven ensures that the material evenly melts and coats the mold, while the cooling chamber solidifies the product once the desired shape is reached. Additionally, accurate temperature control is vital for uniformity and minimizing defects.
Choosing suitable materials is another key aspect of successful rotational molding. Polyethylene, for example, is a popular choice due to its durability and ease of processability. In contrast, engineered resins can offer enhanced performance characteristics suited for specific applications. It's important to understand the material properties to select the best option for your project’s needs.
Tips for success in rotational molding include regular maintenance of your equipment to prevent downtime and ensure consistency in production. Another tip is to conduct thorough mold design analysis; this can significantly impact the final product quality, so investing time upfront can lead to better outcomes. Finally, always prototype your designs before full production to identify potential issues and refine your process.
Rotational molding is a versatile manufacturing process that allows for the creation of hollow and complex plastic parts. Understanding the step-by-step process is essential for achieving the desired quality and efficiency. The process begins with selecting the right material, often powdered plastic, which is placed in a mold. The mold is then heated while being rotated along two axes, ensuring an even distribution of the material. As the plastic melts, it coats the interior of the mold, forming the desired shape. Once the cooling phase is achieved, the mold is opened, and the final product is removed.
To ensure success in rotational molding, it’s important to follow best practices at each stage. One useful tip is to carefully monitor the heating process; uneven temperatures can result in inconsistent wall thicknesses. Additionally, maintaining a clean and well-maintained mold is crucial to prevent defects. Another tip is to conduct thorough testing of the molds and materials before full-scale production to identify any potential issues early on. By implementing these techniques, manufacturers can enhance their efficiency and produce high-quality products consistently.
| Technique | Description | Best Practice | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Choosing the right grade of resin is critical for the performance of the final product. | Always consult technical data sheets and consider environmental factors. | Using a resin that is incompatible with the mold design. |
| Mold Design | Molds must be designed to allow for even heating and cooling of the material. | Incorporate proper draft angles and surface textures. | Poor mold design can lead to defects in the product. |
| Process Temperature | Maintaining the right temperature during the molding process is essential for material fusion. | Use temperature controllers to ensure consistency. | Fluctuations in temperature can cause uneven wall thickness. |
| Cooling Phase | Controlled cooling is critical to prevent warping and shrinkage. | Ensure molds are cooled uniformly. | Rapid cooling can lead to cracking in larger parts. |
| Quality Control | Implementing a robust QC process is vital for identifying defects. | Regularly inspect and test products during production. | Neglecting quality checks can lead to costly returns. |
Rotational molding, while an effective process for creating hollow plastic products, presents several common challenges that manufacturers must navigate. One significant challenge is achieving uniform wall thickness throughout the molded part. According to a recent industry report, variations in wall thickness can lead to functionality issues and increased material waste, with as much as 20% of the material potentially being discarded. To address this, careful attention must be paid to the design of the mold and the selection of the appropriate resin. Implementing consistent rotation speeds and angles can also aid in ensuring that resin evenly coats the mold surface, thus promoting a uniform thickness.
Another prevalent issue is the temperature control during the heating and cooling phases of the process. A study indicated that inadequate temperature regulation can result in defects such as warping or sink marks, negatively impacting product quality. To mitigate these risks, manufacturers are advised to invest in reliable temperature monitoring systems that provide real-time data throughout the molding cycle. Ensuring that the mold is preheated correctly and maintaining optimal temperature during the cooling phase can significantly enhance the end product's durability and appearance, leading to increased customer satisfaction and reduced rework costs.
The field of rotational molding is experiencing innovative trends that are reshaping manufacturing processes and enhancing the capabilities of this versatile technique. One of the most exciting developments is the integration of advanced materials, such as biodegradable plastics and engineering-grade polymers, which are not only improving the durability and functionality of molded products but also addressing environmental sustainability concerns. These materials enable manufacturers to create lighter, stronger, and more resilient parts while minimizing their ecological footprint, paving the way for a greener future in manufacturing.
Furthermore, the adoption of smart technologies, including automation and real-time monitoring systems, is revolutionizing the rotational molding process. These technologies allow for enhanced precision and efficiency, leading to reduced cycle times and improved quality control. For instance, the use of cloud-based software for data analysis enables manufacturers to predict potential issues before they arise, streamlining production and reducing waste. As sensors and IoT devices become more prevalent in the industry, manufacturers can expect significant advancements in customization and flexibility, allowing for tailored solutions that meet specific customer needs. These trends signal a bright future for rotational molding, characterized by innovation and adaptability in meeting market demands.






