Thermoforming is a vital process in the plastic production industry, enabling the creation of a wide range of products with efficiency and precision. As industry expert Dr. Emily Carter states, “Mastering thermoforming techniques not only enhances product quality but also significantly reduces production costs.” This statement encapsulates the essence of mastering thermoforming, highlighting both the economic and practical benefits of refining these techniques.
In an era where sustainability and efficiency are increasingly prioritized, understanding thermoforming methods becomes essential for manufacturers. The ability to manipulate thermoplastics into desired shapes while minimizing material waste is crucial for staying competitive. The intricacies of this technique, from material selection to mold design, can have profound impacts on the overall production process. By focusing on advanced thermoforming strategies, companies can not only streamline their operations but also contribute to a greener manufacturing landscape.
As this article delves into various thermoforming techniques, readers will gain insights and actionable advice to elevate their production capabilities. Whether you are a novice or an experienced professional in the thermoforming industry, the knowledge shared here aims to empower you with the skills necessary to excel in this dynamic field.
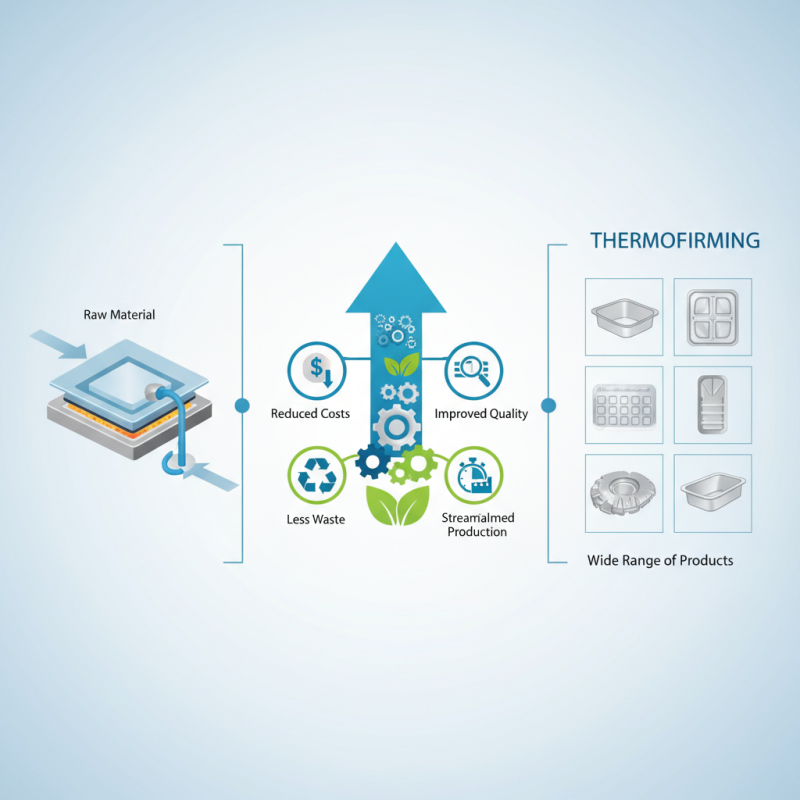
Thermoforming is a widely used manufacturing process for shaping plastic materials into specified forms, primarily utilizing heat to soften and mold the plastic sheets. This technique is fundamental in various industries, including packaging, automotive, and consumer goods, owing to its efficiency and adaptability. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the thermoforming market is expected to reach $18.3 billion by 2026, driven by its increasing application in sustainable packaging solutions and lightweight materials for automobiles.
Mastering the principles of thermoforming involves understanding the key stages of the process, which include heating, forming, and cooling. During the heating phase, the plastic sheet is brought to its forming temperature, ensuring it becomes pliable enough to be shaped. The subsequent forming stage can employ vacuum, pressure, or mechanical methods to achieve the desired product shape. Finally, in the cooling phase, the material retains its form, solidifying as it returns to a lower temperature. This understanding of the thermal properties of materials is critical for optimizing production cycles and ensuring product consistency.
**Tips:** Always conduct pre-production tests to identify the ideal heating times and temperatures for your specific materials, as variations can lead to inconsistencies in thickness and strength. Regular maintenance of your thermoforming equipment is crucial to reduce downtime and maintain production efficiency. Additionally, staying updated on industry trends and innovations can provide insights into new techniques and materials that enhance the thermoforming process and overall product quality.
The thermoforming process is a vital technique in plastic production, allowing manufacturers to create a variety of shapes and products efficiently. The process begins with selecting a suitable thermoplastic sheet, which is then heated until it becomes pliable. Proper temperature control is crucial at this stage, as overheating can lead to material degradation while underheating can prevent proper forming. Once the material is adequately heated, it is placed over a mold, where a vacuum or pressure is applied to inflate or shape the material into the desired form.
After the material has been formed, it's essential to cool it down while still in contact with the mold to maintain the shape. This cooling process can vary in time depending on the thickness of the plastic used. Once cooled, the formed plastic is trimmed and any excess material is removed. Finally, the finished products undergo quality checks to ensure they meet design specifications and standards. Mastering each step of this process, from heating to cooling, is critical for efficient production and achieving high-quality thermoformed products.
Choosing the right materials for thermoforming is critical to maximizing efficiency and ensuring high-quality production in the plastics industry. Thermoforming frequently utilizes thermoplastic materials, such as ABS, PVC, and polycarbonate, owing to their excellent moldability and thermal properties. According to a report by the Plastics Industry Association, the demand for polycarbonate is expected to reach 3.6 million metric tons by 2026, driven by its strength, clarity, and impact resistance, making it an ideal choice for demanding applications.
When selecting materials for thermoforming, it is essential to consider factors such as the end-use application, required mechanical properties, and cost-effectiveness. For example, ABS provides a good balance of toughness and rigidity, which is favorable in automotive and consumer goods applications. A 2021 study published in the Journal of Polymer Science indicated that materials that possess better thermal stability tend to result in higher production yields and less scrap. Furthermore, advancements in bio-based polymers are gaining traction, as companies seek sustainable options to reduce their environmental impact, with projections suggesting a growth rate of 22% for these materials over the next five years.
Understanding the specific requirements of a project, including thermal resistance, transparency, and weight, will guide manufacturers in selecting materials best suited for their desired outcomes. Collaborating closely with material suppliers can also provide insights into innovations in polymer technology that could enhance the thermoforming process, ultimately leading to more efficient production cycles and superior product performance.
Optimizing thermoforming efficiency is essential for maximizing production rates and minimizing material waste in the plastic manufacturing industry. According to a report by the Freedonia Group, the demand for thermoformed plastic products is projected to grow by 4.6% annually through 2023, indicating a robust market that requires efficient production techniques to keep up with rising consumer expectations.
One effective approach to enhancing thermoforming efficiency is adopting advanced processing technologies, such as in-line molding systems, which can significantly reduce cycle times and improve overall throughput. This shift not only enhances productivity but also allows for better quality control throughout the manufacturing process.
Additionally, material selection plays a crucial role in optimizing thermoforming. A study published by Plastics Technology highlights that using thinner gauge materials with superior thermoforming characteristics can lead to significant cost savings and reduced energy consumption. For instance, switching to high-performance polymers can decrease material waste by up to 30%, which in turn contributes to sustainability goals within the industry.
Furthermore, incorporating automation as part of the production line streamlines operations, reducing labor costs and increasing precision, ultimately leading to improved cycle efficiency and more consistent product quality. By focusing on these techniques, manufacturers can achieve greater operational efficiency and maintain competitiveness in a rapidly evolving market.

Thermoforming, while a popular method for plastic production, presents several challenges that can hinder efficiency and product quality. One common issue is material wrinkling, which often occurs due to uneven heating or improper material selection. To mitigate this, it's crucial to employ uniform heating techniques and to choose thermoplastics that have consistent thermal properties. Additionally, pre-forming tests can help ensure that materials are optimal for the desired application, helping prevent defects down the line.
Another challenge faced during thermoforming is warping of the finished product, which can happen as the material cools too quickly or unevenly. To avoid this, it is recommended to control the cooling rate by using temperature-controlled molds. Proper mold design, including the use of adequate venting channels, can also assist in achieving an even cooling process. Furthermore, training operators to recognize and address these issues quickly can enhance efficiency and maintain high production standards, ensuring that the thermoforming process runs smoothly.






