Choosing the right plastic resin for your project is a critical decision that can significantly influence the performance, cost, and sustainability of your final product. According to the latest report by Smithers Pira, the global plastic resin market is projected to reach $650 billion by 2025, fueled by the increasing demand for lightweight, durable materials across various industries, including automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. The vast array of plastic resins available today, from polycarbonate to polypropylene, makes the selection process both an opportunity and a challenge for engineers and product developers.
Understanding the unique properties and applications of different plastic resins is essential for optimizing design and functionality. The right choice can enhance product durability, impact resistance, and thermal stability, which are particularly important in applications exposed to extreme conditions. For instance, research by the Plastics Industry Association highlights that high-performance resins can offer up to 50% weight reduction compared to traditional materials, leading to improved fuel efficiency in transportation. Therefore, a thorough assessment of project requirements, coupled with insights from industry reports, is crucial for making an informed decision that meets both technical specifications and budgetary constraints.

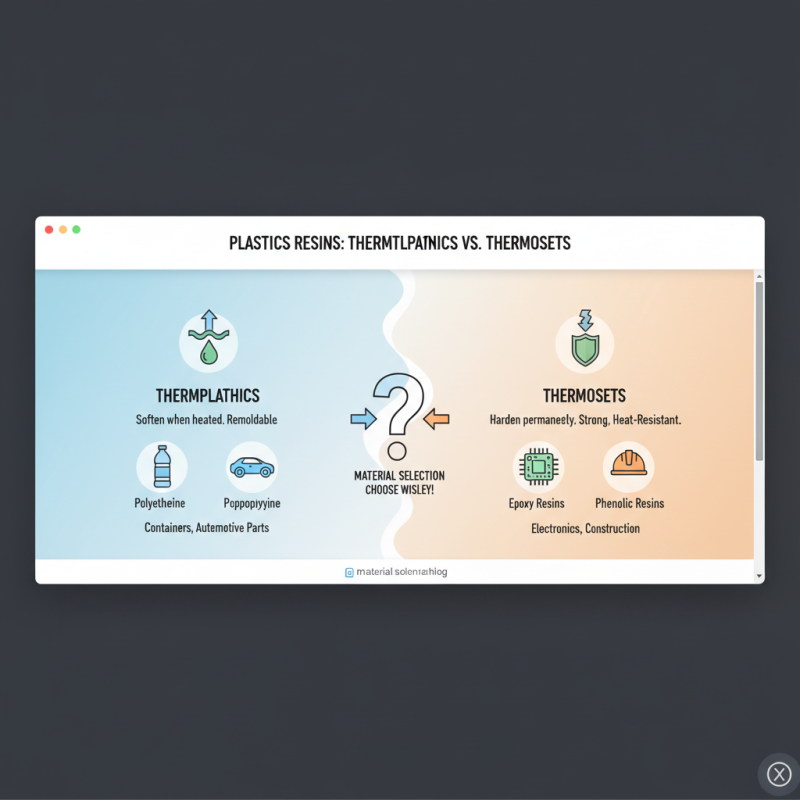
Understanding plastic resins is crucial for selecting the right material for your project. Plastic resins are categorized into two main types: thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. Thermoplastics, like polyethylene and polypropylene, soften when heated and can be re-molded multiple times. This flexibility makes them suitable for products ranging from containers to automotive parts. On the other hand, thermosetting plastics, such as epoxy and phenolic resins, harden permanently after curing, providing superior strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for applications in electronics and construction.
When choosing a resin, consider the mechanical properties, compatibility with other materials, and processing methods required for your project. Each type of resin has specific advantages and limitations based on its chemical structure. For instance, if your project demands high-impact resistance and temperature stability, a thermosetting resin may be the better choice.
Tips: Always conduct a compatibility test when mixing resins with different additives or fillers to avoid compromising the material's integrity. Additionally, thoroughly evaluate the environmental conditions your final product will face, such as exposure to humidity or chemicals, to ensure long-term performance. Don't overlook the importance of understanding the flow characteristics of the resin, as this can significantly affect the molding process and overall quality of the finished item.
When selecting the appropriate plastic resin for a project, it is crucial to assess specific project requirements that align with the intended application. The first consideration is the mechanical properties needed for the final product. According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), parameters such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility are pivotal for determining the right material. For instance, projects requiring high impact resistance may benefit from using polycarbonate resins, which, according to industry reports, exhibit superior toughness and durability compared to standard acrylics.
Another critical aspect to consider is the thermal and chemical resistance of the resin. A report from the Plastics Industry Association highlights the importance of understanding the operating environment of the end product. For example, if the application involves exposure to solvents or high temperatures, selecting a resin with appropriate thermal stability and chemical resistance becomes imperative. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), for instance, maintains its integrity under harsh conditions, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications where exposure to various chemicals is common. By carefully evaluating these factors, project managers can choose a resin that not only meets performance criteria but also ensures longevity and reliability in the application.
When selecting the right plastic resin for a project, understanding the mechanical and thermal properties of different materials is crucial. Mechanical properties such as tensile strength, flexibility, and impact resistance directly influence how a resin will perform under stress. For instance, a project requiring high durability may benefit from a resin with high tensile strength, while applications that demand flexibility would require materials that exhibit sufficient elongation before breaking. Evaluating these properties helps in determining how well the resin can withstand operational conditions, ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of the final product.
Equally important are the thermal properties of resins, which include thermal conductivity, heat deflection temperature, and thermal expansion. These properties dictate how a resin reacts to temperature fluctuations, making them essential for applications involving heat exposure or requiring thermal stability. For instance, in applications where the material may encounter high temperatures, selecting a resin with a high heat deflection temperature ensures that it maintains its shape and performance. By carefully comparing the mechanical and thermal properties of various plastic resins, one can make an informed choice that aligns with the specific demands of the project, leading to optimal performance and durability.
When evaluating cost and availability of different plastic resins, it is essential to consider both the market dynamics and the specific requirements of your project. The cost of plastic resins can vary significantly based on factors such as type, quality, and production processes. For instance, commodity resins tend to be more economical due to their widespread production and availability, whereas specialty resins, which may offer enhanced properties like superior durability or temperature resistance, generally come with a higher price tag. Conducting a thorough market analysis can help in identifying which resins fit within your budget while still meeting the necessary performance criteria.
Availability is another critical aspect to consider, as not all resins are equally accessible in all regions. Supply chain disruptions, raw material shortages, and regional demand fluctuations can all impact the availability of specific plastic resins. It's advisable to maintain close communication with suppliers to understand their inventory levels and lead times, ensuring that your chosen resin can be sourced reliably. Furthermore, exploring alternatives or substitutes that offer similar properties can not only broaden your options but also aid in mitigating risks associated with availability. Together, these evaluations will guide you in selecting the most appropriate plastic resin for your project's unique needs.
| Plastic Resin Type | Cost (per kg) | Availability | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | $1.00 | Widely Available | Bottles, Plastic Bags, Toys |
| Polypropylene (PP) | $1.20 | Widely Available | Packaging, Automotive Parts, Textiles |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | $1.50 | Moderately Available | Pipes, Vinyl Siding, Flooring |
| Polystyrene (PS) | $1.10 | Widely Available | Insulation, Disposable Cutlery, Packaging Foam |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | $2.00 | Moderately Available | Lego Bricks, Automotive Parts, Consumer Electronics |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | $2.50 | Less Available | Lenses, Safety Glasses, Bulletproof Glass |
When selecting plastic resins for any project, sustainability plays a crucial role in the decision-making process. The environmental impact of plastic materials is a significant concern, prompting designers and manufacturers to consider alternative options that minimize harm to the planet. This includes evaluating the entire lifecycle of the resin, from raw material extraction and production processes to usage and end-of-life disposal. Choosing resins derived from renewable resources or those that are biodegradable can significantly reduce a project’s carbon footprint.
Additionally, the recyclability of plastics should not be overlooked. Opting for resin types that can be easily recycled encourages a circular economy, where materials are reused rather than discarded. Understanding local recycling capabilities and regulations can help in selecting resins that are more likely to be processed responsibly after their initial use. By prioritizing these sustainability considerations, project creators can contribute positively to environmental preservation while still meeting their functional and aesthetic needs in material selection.






