Aluminum casting is a fascinating process that transforms raw metal into precise parts. This method has been used for decades and remains vital in various industries. The process begins with molten aluminum, which is poured into molds. Once cooled, it takes the shape of the mold, resulting in a strong, lightweight part.
However, aluminum casting is not without its challenges. Contamination can occur if the metal is not properly handled. Air bubbles and impurities may weaken the final product. It is essential to maintain high standards throughout the casting process to ensure durability and quality.
Understanding aluminum casting involves recognizing both its potential and limitations. It is a method that marries creativity with precision. Yet, it requires constant attention to detail. As industries evolve, so too must the practices around aluminum casting. There remains much to learn and improve within this art form.

Aluminum casting is a crucial process in various industries. It involves pouring molten aluminum into molds to create specific shapes. This method allows for high precision and intricate designs. According to recent industry reports, the aluminum casting market is expected to grow significantly. It should reach approximately $43 billion by 2026. This growth reflects the material's versatility and importance in manufacturing.
Understanding aluminum casting is vital. The process offers several advantages, such as excellent corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio. These properties make aluminum an ideal choice for automotive and aerospace applications. However, challenges persist. Issues like porosity can affect the quality of the final product. Companies must focus on improving their processes to address these concerns.
Aluminum casting fills a unique role in product development. Many sectors rely on its lightweight nature. However, not all casting techniques are equally effective. Some methods may lead to defects, impacting the final product's performance. Recognizing these nuances is essential for engineers and manufacturers. Continuous improvement in aluminum casting practices is necessary to maximize the benefits it offers.
Aluminum casting is a fascinating field. It involves various processes to shape aluminum into desired forms. Each method has unique characteristics, advantages, and challenges. Understanding these processes can enhance manufacturing decisions.
One common method is sand casting. This process uses sand molds to create parts. It’s relatively affordable for small production runs. However, it may not always provide the finest surface finish. This can lead to extra finishing work later.
Die casting is another popular choice. It allows for high-volume production with precise dimensions. It's ideal for complex shapes and reduces waste. Yet, it requires significant upfront costs for tooling. Evaluate your production needs carefully before choosing this method.
Tips: Always consider the specific needs of your project. Each process has trade-offs. Research thoroughly to avoid costly mistakes. Working with experienced professionals can also prevent errors. Don’t overlook the importance of quality control in any casting process.
This bar chart illustrates the production rates of various aluminum casting processes. Die casting shows the highest production rate, while investment casting has the lowest. Understanding these rates helps manufacturers choose the appropriate method based on their production needs.
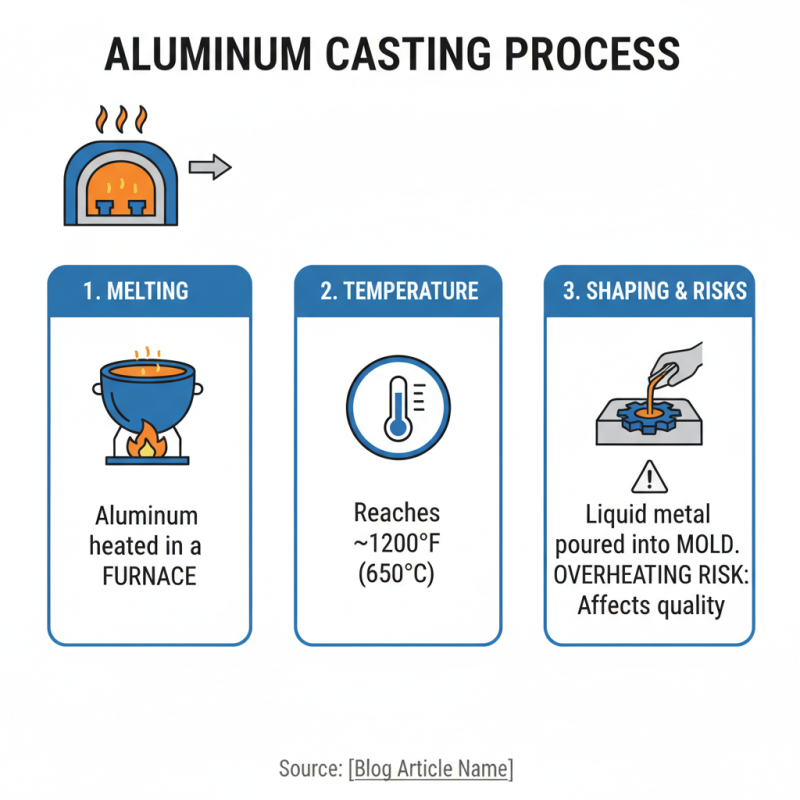
Aluminum casting is a fascinating process that shapes metal into useful forms. The process begins with melting aluminum in a furnace. The metal reaches a temperature near 1,200 degrees Fahrenheit. This is where the magic happens, but it’s not without risks. The furnace can overheat, affecting the quality of the aluminum.
Once melted, the aluminum is poured into prepared molds. These molds determine the final shape of the castings. It’s crucial to ensure no debris contaminates the mold. Inadequate cleaning can result in defects. After pouring, the aluminum cools and solidifies. This stage is delicate; rapid cooling might create cracks.
Finally, the casting is removed from the mold. This is an exciting moment, yet it requires careful handling. Some castings might need additional processing, like machining or finishing. This final touch enhances the product's quality but can also reveal flaws. Each step requires precision to ensure a successful outcome.
Aluminum casting is widely used across various industries due to its unique properties. Lightweight yet strong, aluminum is ideal for automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Car manufacturers often use aluminum components to enhance fuel efficiency. In aerospace, the reduction in weight leads directly to increased performance.
Common applications include engine parts, transmission housings, and intricate machine casings. The versatility of aluminum allows for complex shapes, meeting the demands of modern manufacturing. In the construction sector, aluminum castings are used for fixtures and fittings. They provide durability and resistance to corrosion, suitable for outdoor environments.
Tips: When choosing aluminum castings, consider the specific needs for strength and weight. Look for suppliers who provide samples. Testing can expose imperfections or flaws that may arise during production. Regular maintenance of aluminum parts is key to longevity. Remember, not every casting process yields perfect results; some may require adjustments. Reflecting on these factors can lead to better decisions in your projects.

Aluminum casting offers several advantages. It’s lightweight yet strong, making it ideal for various applications. The process allows for intricate designs, suitable for complex shapes. These benefits lead to lightweight parts that enhance efficiency in products like vehicles and machinery.
However, aluminum casting also presents challenges. One major issue is controlling the cooling rate. Uneven cooling can cause defects, like cracks and voids. Additionally, the recycling of aluminum requires care. Poor-quality recycled materials can affect the final product’s strength.
Another concern is the high initial setup cost for casting molds. This can be a barrier for small manufacturers. Quality control is crucial, yet sometimes hard to achieve. Techniques need constant refinement. Understanding these challenges is vital for successful projects. Balancing advantages and issues requires ongoing effort and innovation.